When building or upgrading your PC, one of the most important components you must choose is the power supply unit (PSU). It might seem like a small piece of the puzzle compared to your CPU or GPU, but a power supply is the heart of your system. It powers everything from your motherboard to your hard drive and graphics card. If you pick the wrong PSU, your system can face issues like instability, random shutdowns, or even permanent damage.
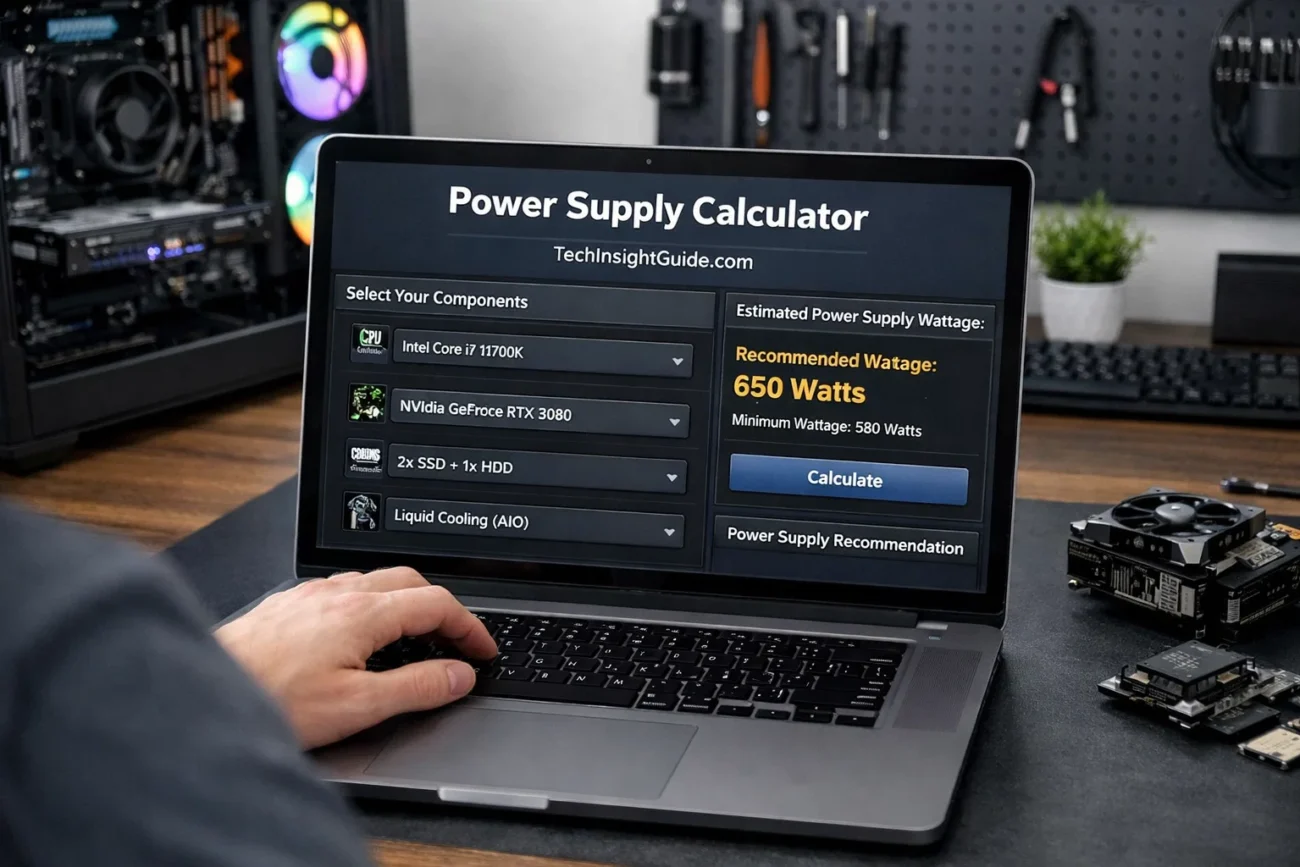
That’s where the power supply calculator comes in handy. A power supply calculator helps you figure out exactly how much wattage your PC components need to run smoothly. Without this, you might end up with a PSU that’s either underpowered or unnecessarily overpowered. Both scenarios can lead to wasted money or damage to your system in the long run.
This tool is especially helpful if you plan to upgrade your system or build a new one from scratch. It considers every component in your system—CPU, GPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals—and calculates the wattage that your PSU should supply. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what a power supply calculator is, how it works, and why it’s essential for every PC builder and upgrader.
What Is a Power Supply Calculator?
A power supply calculator is a tool, usually available online, that helps you calculate how much power your computer system requires from its power supply unit (PSU). This tool factors in various components of your PC like the CPU, GPU, RAM, motherboard, storage, and cooling fans. The calculator works by estimating the total wattage your components will draw during usage and recommends an appropriate PSU wattage.
Typically, the calculator asks you to input details about the specific parts you’re using, such as your CPU model, GPU model, number of drives, and the type of cooling system you have. Once you enter this information, the calculator processes the data and provides an output in watts that will guide you in selecting a PSU of the correct size. For instance, a high-end gaming PC with a powerful graphics card may need a PSU that delivers at least 750 watts of power, while a basic system could run smoothly with only 400 watts.
An important feature of most power supply calculators is the buffer it provides. They often recommend adding an extra 20–30% wattage buffer on top of your required wattage. This buffer ensures that your PSU can handle any sudden spikes in power demand, such as during gaming or heavy workloads, without causing system instability.
How Does a Power Supply Calculator Work?
When you use a power supply calculator, it essentially helps you estimate the wattage required for all the components in your computer system. The calculator works by adding the power consumption of each part. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Step 1: Input Information
You start by entering details about your computer system, including:
- CPU Model: The power consumption of your CPU can vary significantly depending on whether it’s an energy-efficient model or a high-performance one.
- GPU Model: The graphics card is typically the most power-hungry component in a gaming or workstation PC. High-end GPUs like the NVIDIA RTX series draw more power than lower-end models.
- Storage Devices: If you have multiple storage drives, such as SSDs or HDDs, each one consumes power, though the amount is relatively small compared to the CPU or GPU.
- Other Components: These include RAM, motherboard, cooling systems, and any additional accessories like fans.
Step 2: Calculation Process
Once you input the details, the calculator sums up the wattage requirements of each component. It uses known power consumption data for each part based on its specifications. For example, a typical mid-range graphics card might use 200W, while a powerful gaming GPU can require up to 450W.
Step 3: Buffer Addition
After calculating the total power draw, the calculator often recommends a buffer of 20–30%. This ensures that your PSU will not be under constant strain and can handle future upgrades or unexpected power surges. This safety margin prevents your system from crashing during high-demand moments like gaming or video editing.
Why Is a Power Supply Calculator Important?
Using a power supply calculator is crucial for several reasons. One of the primary reasons is to ensure that your system gets enough power to function properly. But there’s more to it than just avoiding power shortages.
Avoiding Instability and System Crashes
Without a properly sized PSU, your system may crash during intensive operations like gaming, video editing, or running multiple programs at once. A power supply calculator ensures that your PSU meets the minimum power requirements to prevent these problems.
Protecting Your Components
If your PSU is too weak, it can lead to voltage fluctuations that may damage your sensitive components. On the other hand, an oversized PSU doesn’t pose a direct risk, but it’s inefficient and costs more money than necessary. Calculators ensure you get the right fit without wasting resources.
Future-Proofing Your Build
When planning a system, a power supply calculator gives you insights not just for your current needs, but for future upgrades as well. Whether you’re adding more storage or upgrading your GPU later, knowing your PSU wattage in advance allows for future-proofing your system.
The Key Components That Affect Power Needs
Each component in your system draws power. But some parts use significantly more than others, especially in gaming PCs or high-end workstations. Here’s a breakdown of the key components that affect power consumption:
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The GPU is often the biggest consumer of power in a gaming or graphics-intensive PC. High-performance GPUs like those from NVIDIA or AMD can require anywhere between 200W to 450W, depending on the model. In fact, if you’re a gamer or into 3D rendering, the GPU will likely determine how much wattage your PSU needs.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
While the CPU doesn’t use as much power as the GPU, it still contributes to the overall consumption. High-performance CPUs, especially those with many cores (like Intel i9 or AMD Ryzen 9), will draw more power. Typically, CPU usage falls between 65W to 150W.
Storage and Drives
Each drive (HDD, SSD) uses a small amount of power—usually between 5W to 10W each. However, if you have multiple drives, the total wattage can add up, so these should be included in your PSU calculation.
Cooling Systems and Fans
Though individually these components don’t consume much power, many cooling fans can add up. Each fan can use around 1W to 5W. If you plan on using multiple cooling fans, it’s important to account for them as well in the calculation.
How to Use a Power Supply Calculator
Using a power supply calculator is simple and straightforward. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Find a Trusted Power Supply Calculator
There are many trusted online calculators you can use. Some of the most popular options are from companies like Corsair, Cooler Master, Seasonic, and MSI. Most of them offer a free, user-friendly interface.
Step 2: Input Your System Specifications
You will be asked to input various details about your PC, including your CPU, GPU, number of storage devices, and cooling system. Some calculators will also ask about future upgrades, like adding more RAM or overclocking your GPU. This step is key because it gives you an estimate of your current and future needs.
Step 3: Review Your PSU Recommendation
Once the calculator has processed your inputs, it will provide a wattage recommendation for your PSU. For example, if your system requires 450W but you plan on upgrading to a better GPU later, the calculator might recommend a 600W PSU to accommodate future power needs.
Step 4: Choose Your PSU
Based on the recommendation, you can choose a PSU with the suggested wattage. If you’re unsure, it’s always better to go for a slightly higher wattage PSU to account for future upgrades or power surges.
Common Myths About Power Supplies
There are several misconceptions about power supplies that could lead to confusion:
Myth 1: More Watts Equals Better Performance
The wattage of your PSU does not directly impact your computer’s performance. A higher-wattage PSU doesn’t make your PC run faster. It simply ensures the system gets enough power. What matters is whether your PSU provides consistent and stable power, not just higher wattage.
Myth 2: A 500W PSU Can’t Run a Gaming PC
Many entry-level 500W PSUs can handle a mid-range gaming PC. However, if you’re running high-end components like top-tier graphics cards and multiple storage devices, a 750W PSU might be more appropriate. The calculator will guide you based on your actual needs, making sure you get just the right amount.
Myth 3: All PSUs Are the Same
Not all PSUs are built the same. The efficiency of a PSU matters. Look for 80+ rated PSUs for optimal performance. Higher efficiency means less power loss as heat and more money saved over time.
Read More: MyGameRank Gaming Guides: Master Your Skills and Boost Your Rankings
Conclusion: Make the Right PSU Choice for a Smooth Experience
Choosing the right power supply is more than just picking the biggest PSU you can find. It’s about matching your system’s requirements with the correct wattage, ensuring future-proofing, and avoiding instability. A power supply calculator is an easy-to-use tool that ensures you’re selecting the right PSU for your needs.
By using a power supply calculator, you ensure that your system will run smoothly and efficiently, with enough headroom for future upgrades. Don’t risk underpowering or overpaying for a PSU that is either too small or too big. Take advantage of these online tools to get the perfect fit for your setup.